library(RaCE.NMA)
library(ggplot2)
library(dplyr)
library(cowplot)
library(gridExtra)
library(reshape2)In this vignette, we provide code to reproduce the analyses presented in the paper associated with this R package. Specifically, we reproduce two simulation studies (Sections 3.1 and 3.2) and a case study (Section 4). We assume knowledge of the associated R package functions; please refer to the “Tutorial” and “Reference” pages for more information.
Reproduction of Simulation Study 1 (Section 3.1)
The following code reproduces Figure 1.
s <- 0.1
g1a<-ggplot()+scale_x_continuous(limits=c(-3*s,1+3*s))+
stat_function(fun = dnorm, args = list(mean = 0, sd =s))+
stat_function(fun = dnorm, args = list(mean = 1, sd =s))+
theme_bw()+labs(x=" ",y="Density",title=expression(hat(sigma)~"=0.1"))+
theme(panel.grid.minor = element_blank(),panel.grid.major.y = element_blank())
s <- 0.3
g1b<-ggplot()+scale_x_continuous(limits=c(-3*s,1+3*s))+
stat_function(fun = dnorm, args = list(mean = 0, sd =s))+
stat_function(fun = dnorm, args = list(mean = 1, sd =s))+
theme_bw()+labs(x="Posterior Intervention Effects",y=element_blank(),title=expression(hat(sigma)~"=0.3"))+
theme(panel.grid.minor = element_blank(),panel.grid.major.y = element_blank())
s <- 0.5
g1c<-ggplot()+scale_x_continuous(limits=c(-3*s,1+3*s))+
stat_function(fun = dnorm, args = list(mean = 0, sd =s))+
stat_function(fun = dnorm, args = list(mean = 1, sd =s))+
theme_bw()+labs(x=" ",y=element_blank(),title=expression(hat(sigma)~"=0.5"))+
theme(panel.grid.minor = element_blank(),panel.grid.major.y = element_blank())
grid.arrange(g1a,g1b,g1c,nrow=1)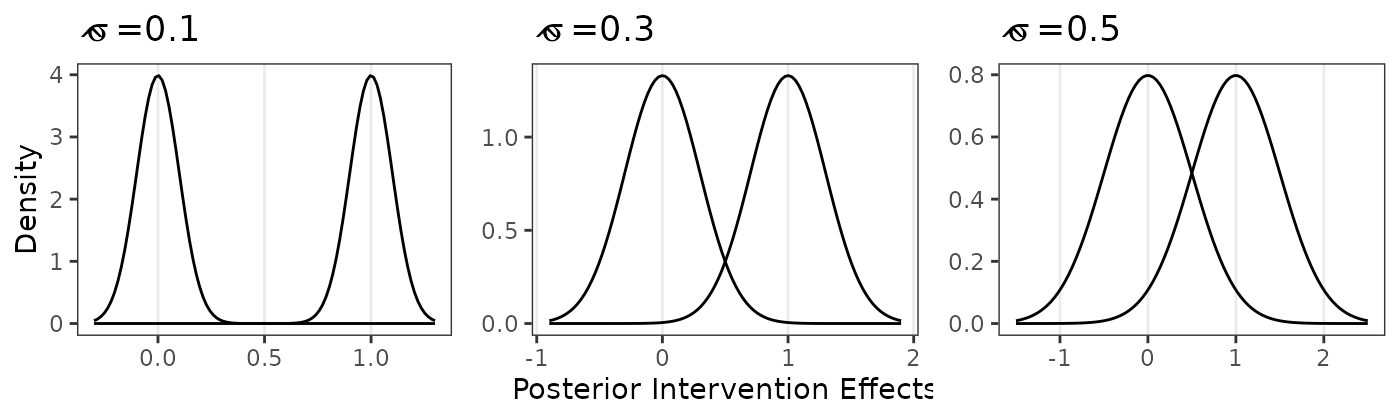
The following code reproduces Figure 2: First, we perform a simulation study. Second, we create the figure.
## Perform simulation study
set.seed(1)
results <- matrix(NA,nrow=0,ncol=6)
for(iter in 1:20){
for(J in c(6,12,18)){
for(K in c(J/3,2*J/3,J)){
for(s in c(0.1,0.3,0.5)){
if(K==J){
ybar <- 1:K
}else{
ybar <- sample(1:K,J,replace=T)
while(length(unique(ybar))<K){ybar <- sample(1:K,J,replace=T)}
}
mcmc <- mcmc_RCMVN(ybar=ybar,s=rep(s,J),mu=mean(ybar),sigma0=max(1,4*sd(ybar)),nu0=ybar,
tau=1,num_iters=3000,nu_reps=2,chains=4,burn_prop=0.5,thin=3,suppressPrint = TRUE)
equal <- posterior_equal <- matrix(NA,nrow=J,ncol=J)
for(i in 1:(J-1)){for(j in (i+1):J){
equal[i,j] <- ifelse(ybar[i]==ybar[j],1,0) # test if treatments are truly equal in mean
posterior_equal[i,j] <- mean(mcmc[,paste0("G",i)] == mcmc[,paste0("G",j)]) # assess if treatments are rank-clustered
}}
results <- rbind(results,c(iter,J,K,s,mean(posterior_equal[equal==1],na.rm=T),mean(posterior_equal[equal==0],na.rm=T)))
}
}
}
}
## Plotting results from simulation study
results <- as.data.frame(results)
names(results) <- c("Iteration","J","K","s","Prob_Clustered","Prob_Distinct")
results$s<-factor(results$s, levels=c(.1,.3,.5),
labels=c(expression(hat(sigma)~"=0.1"),expression(hat(sigma)~"=0.3"),expression(hat(sigma)~"=0.5")))
results$J <- factor(results$J,levels=c(6,12,18),labels=c(expression(J~"= 6"),expression(J~"= 12"),expression(J~"= 18")))
results_melt <- melt(results,id.vars=1:4)
results_melt <- results_melt[!is.nan(results_melt$value),] # drop "cluster" cases when K=J
ggplot(results_melt,aes(x=factor(K),y=value,color=factor(variable,labels=c("Rank-Clustered","Distinct"))))+
facet_grid(s~J,scales="free_x",labeller=label_parsed)+
geom_boxplot(outlier.alpha=0.5,position="identity")+theme_bw()+
scale_color_manual(values=c("skyblue","darkblue"))+
labs(x="Number of Rank-Clusters, K",y="Posterior Rank-Clustering Probability",
color=element_blank())+
theme(legend.position = "bottom",panel.grid.minor = element_blank(),
panel.grid.major.x = element_blank())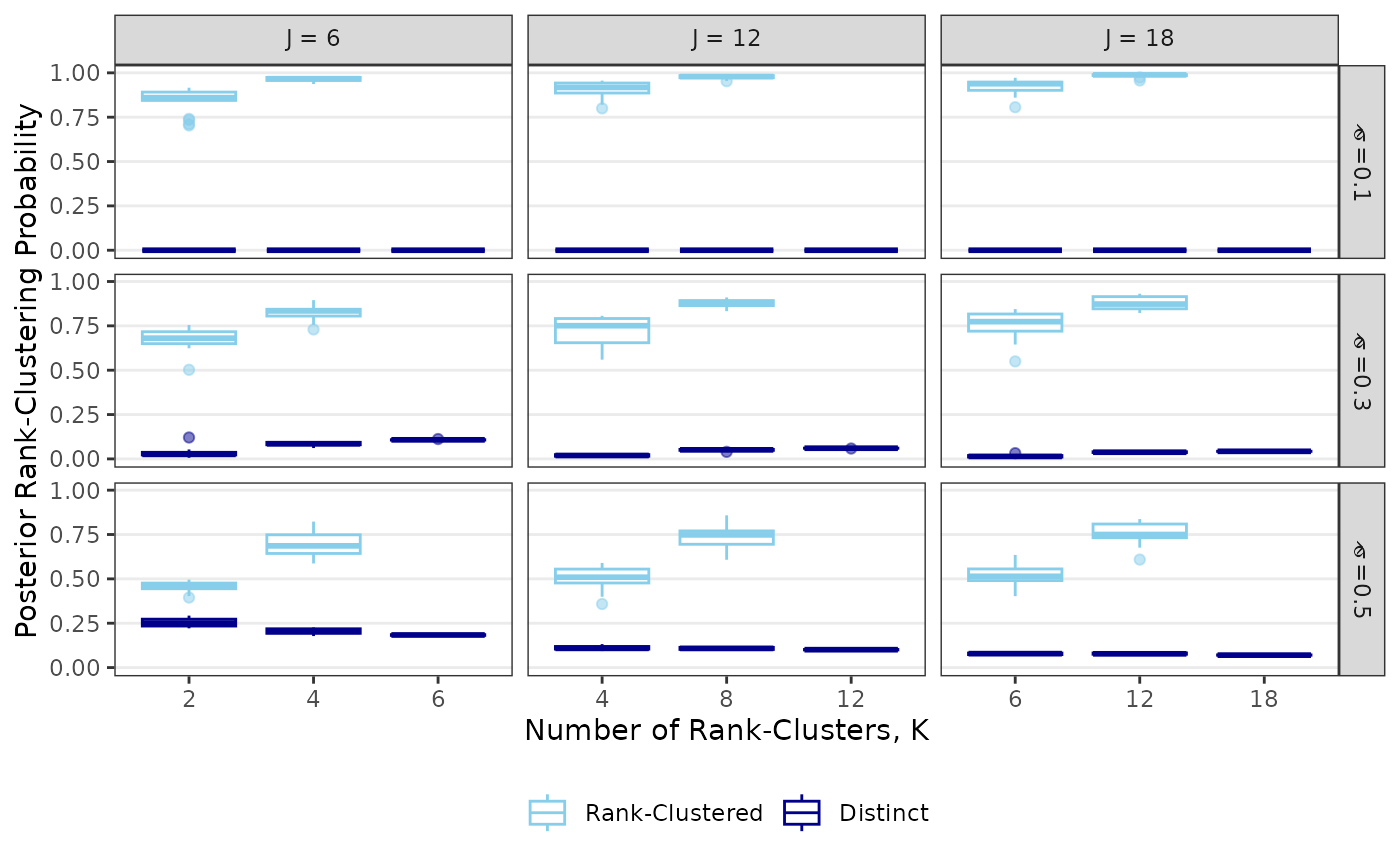
Reproduction of Simulation Study 2 (Section 3.2)
The following code reproduces Figure 3.
J <- 4
ybar <- c(-1,0,1,0)
s <- c(.1,.1,.1,1)
set.seed(2)
data <- matrix(data = rnorm(10000*4,mean=ybar,sd=s), ncol = 4, byrow = TRUE)
ggplot(data.frame(name=1:J,mean=ybar,lower_CI=ybar-1.96*s,upper_CI=ybar+1.96*s),
aes(y=factor(name),x=mean,xmin=lower_CI,xmax=upper_CI))+
geom_point()+geom_linerange()+scale_y_discrete(limits=rev)+
theme_bw()+theme(panel.grid.minor = element_blank(),panel.grid.major.x = element_blank())+
labs(y="Treatment",x="Posterior")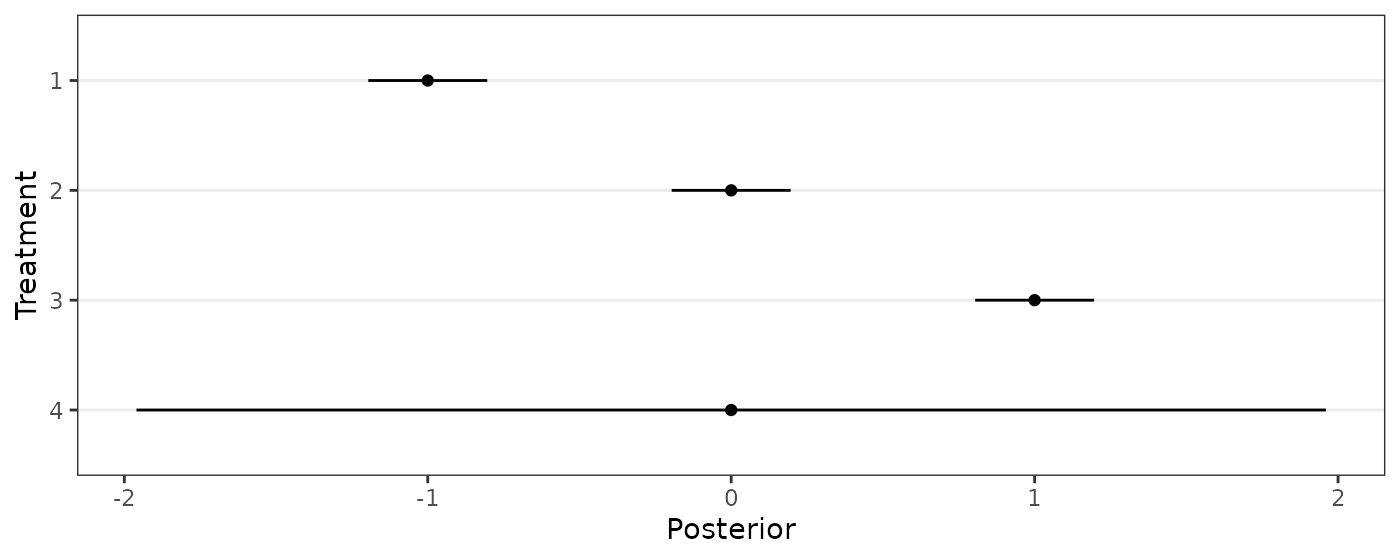
The following code reproduces Table 1: First, we fit the RaCE model to the simulated data. Second, we calculate and display the values in Table 1.
mcmc <- mcmc_RCMVN(ybar=ybar,s=s,num_iters=50000,nu_reps=2,chains=4,burn_prop=0.5,thin=1,suppressPrint = TRUE)
posterior_equal <- matrix(NA,nrow=J,ncol=J)
for(i in 1:(J-1)){for(j in (i+1):J){
posterior_equal[i,j] <- mean(mcmc[,paste0("G",i)] == mcmc[,paste0("G",j)])
}}
round(posterior_equal,2)
## [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
## [1,] NA 0 0 0.18
## [2,] NA NA 0 0.40
## [3,] NA NA NA 0.19
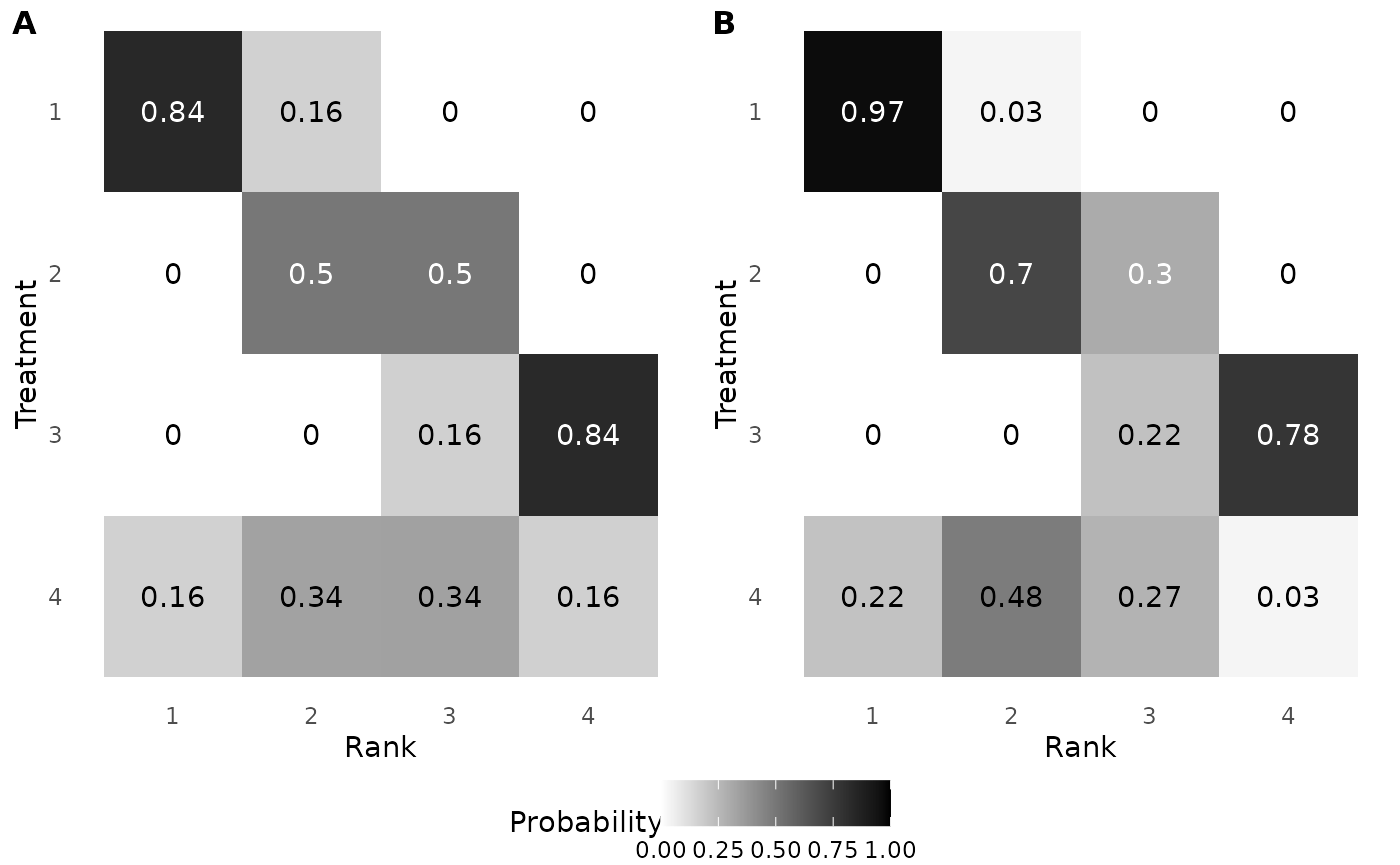
## [4,] NA NA NA NAThe following code reproduces Figure 4: First, we calculate the posterior rank-clustering probability under a traditional model (i.e., assumption of distinct ranks). Second, we calculate the posterior rank-clustering probability based on the RaCE model. Third, we produce the figure.
post_ranks_traditional <- apply(t(apply(data,1,function(mu){rank(mu)})),2,
function(rank){unlist(lapply(1:J,function(j){mean(rank==j)}))})
post_ranks <- apply(t(apply(mcmc[,paste0("mu",1:J)],1,function(mu){rank(mu,ties.method="min")})),2,
function(rank){unlist(lapply(1:J,function(j){mean(rank==j)}))})
g4a<-ggplot(melt(post_ranks_traditional),aes(x=Var1,y=factor(Var2),fill=value))+
geom_tile()+scale_y_discrete(limits=rev)+
scale_x_continuous(breaks=1:4,limits=c(.5,4.5))+
scale_fill_gradient(low="white",high="black",limits=c(0,1))+
labs(x="Rank",y="Treatment",fill="Probability")+theme_minimal()+
theme(panel.grid = element_blank(),legend.position = "bottom")+
geom_text(aes(x=Var1,y=factor(Var2),label=round(value,2)),
color=ifelse(melt(post_ranks_traditional)$value>0.4,"white","black"))
g4b<-ggplot(melt(post_ranks),aes(x=Var1,y=factor(Var2,levels=paste0("mu",1:J),labels=paste0(1:J)),fill=value))+
geom_tile()+scale_y_discrete(limits=rev)+
scale_x_continuous(breaks=1:4,limits=c(.5,4.5))+
scale_fill_gradient(low="white",high="black",limits=c(0,1))+
labs(x="Rank",y="Treatment",fill="Probability")+theme_minimal()+
theme(panel.grid = element_blank(),legend.position = "bottom")+
geom_text(aes(x=Var1,y=factor(Var2,levels=paste0("mu",1:J),labels=paste0(1:J)),label=round(value,2)),
color=ifelse(melt(post_ranks_traditional)$value>0.4,"white","black"))
plot_grid(plot_grid(g4a+theme(legend.position = "none"), g4b+theme(legend.position = "none"),
labels = c('A', 'B'), label_size = 12),
get_plot_component(g4a, 'guide-box-bottom', return_all = TRUE),nrow=2,rel_heights = c(.9,.1)
)
Reproduction of Case Study (Section 4)
We first load the posteriors from Wang et al. (2022) and calculate the mean and covariances of the relative treatment effects.
data("WangPosteriors")
wang_posterior <- mcmc.df[,4:13] # posteriors of non-baseline treatments
ybar <- c(0, apply(wang_posterior,2,mean)) # calculating mean relative treatment effects
cov <- cov(wang_posterior) # calculating covariance of relative treatment effects
cov <- cbind(c(min(apply(wang_posterior,2,var))/10, rep(0,10)), # updating covariance for baseline treatments
rbind(0,cov) )
treatments <- c("R-CHOP","R-CHOP-R","R-Benda","R-Benda-R","R-Benda-R4",
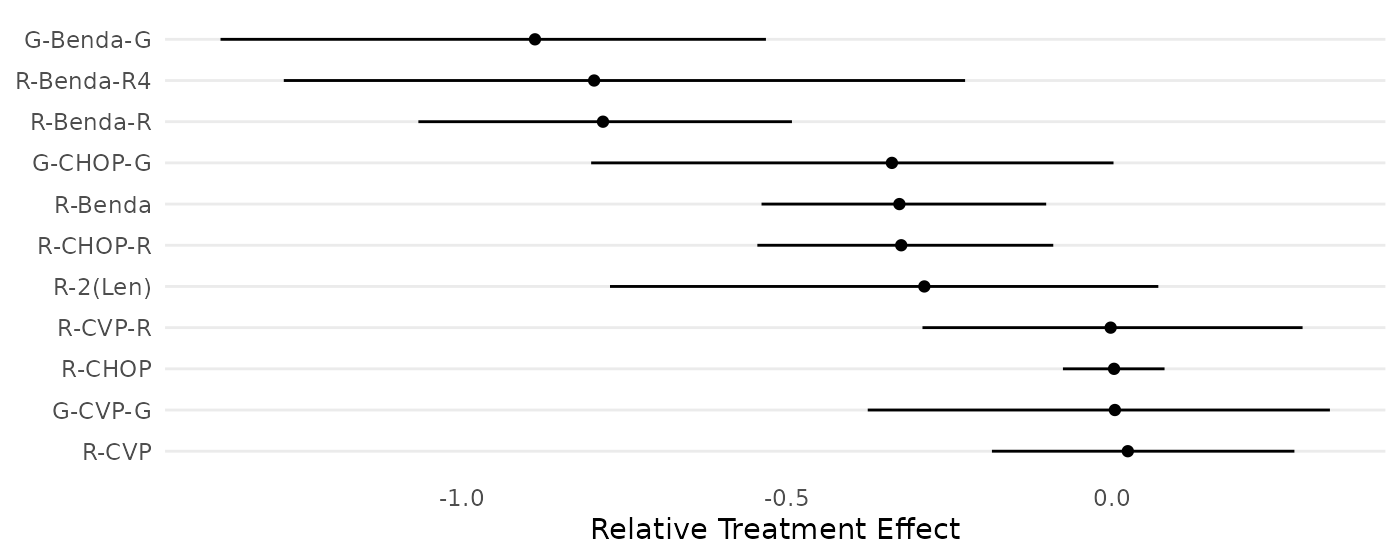
"R-CVP","R-CVP-R","R-2(Len)","G-CVP-G","G-CHOP-G","G-Benda-G")The following code chunk reproduces Figure 5.
forestplot_data <- data.frame(
name=treatments,
mean=ybar,
lower_CI=c(-1.96*sqrt(min(apply(wang_posterior,2,var))/10),apply(wang_posterior,2,function(x){quantile(x,0.025)})),
upper_CI=c(1.96*sqrt(min(apply(wang_posterior,2,var))/10),apply(wang_posterior,2,function(x){quantile(x,0.975)}))
)[-1,] # excluding baseline treatment
forestplot_data$name <- factor(forestplot_data$name,levels=forestplot_data$name[order(forestplot_data$mean)])
ggplot(forestplot_data, aes(y=name, x=mean, xmin=lower_CI, xmax=upper_CI) ) +
geom_point() + geom_linerange() +
scale_y_discrete(limits=rev) + labs(y="Treatment",x="Posterior") +
theme_bw() + theme(panel.grid.minor = element_blank(),panel.grid.major.x = element_blank())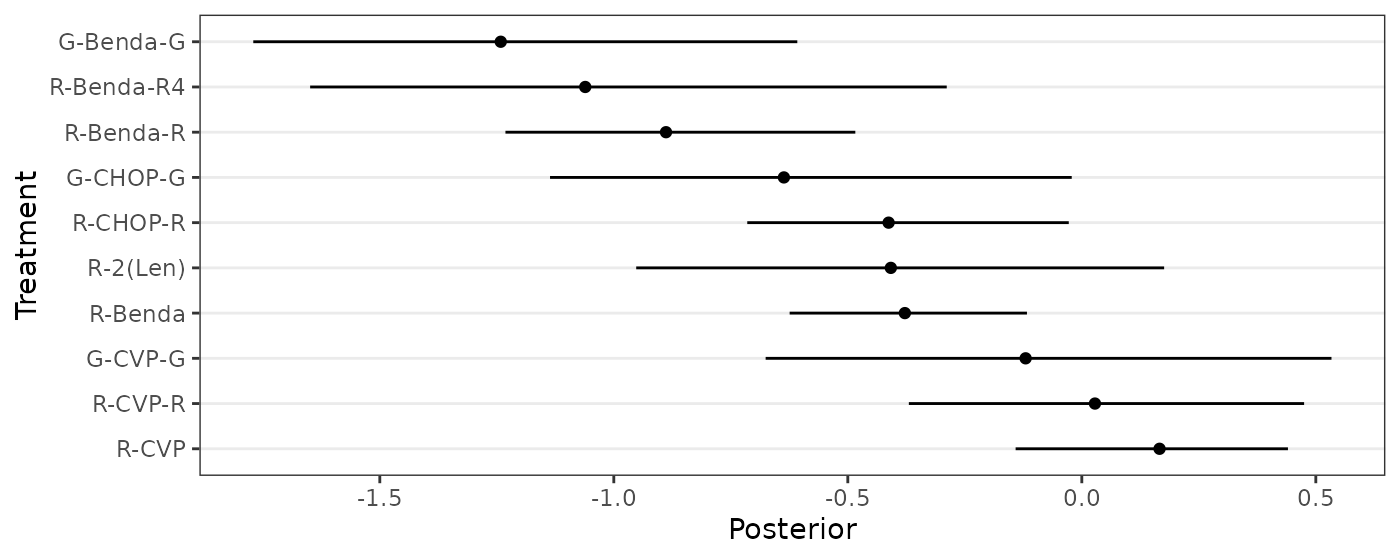
Next, we fit the RaCE model to estimated relative treatment effects from Wang et al. (2022).
mcmc <- mcmc_RCMVN(ybar=ybar, cov=cov, mu0=mean(ybar), sigma0= sqrt(10*var(ybar)),
num_iters=50000,nu_reps=5,chains=4,seed=1,suppressPrint=TRUE)The following code chunk reproduces Figure 6, Figure 7, and Table 2: First, we calculate the values underpinning each graphic. Then, we create each in turn.
# Calculation of values underpinning each graphic
## results based on RaCE model
mcmc_ranks <- as.data.frame(t(apply(mcmc[,4:14],1,function(mu){rank(mu,ties.method="min")})))
mcmc_ranks_probs <- as.data.frame(apply(mcmc_ranks,2,function(ranks){unlist(lapply(1:11,function(j){mean(ranks==j)}))}))
mcmc_ranks_cumprobs <- as.data.frame(apply(mcmc_ranks_probs,2,cumsum))
names(mcmc_ranks) <- names(mcmc_ranks_probs) <- names(mcmc_ranks_cumprobs) <- treatments
## results based on traditional analysis
wang_ranks <- as.data.frame(t(apply(cbind(0,wang_posterior),1,function(mu){rank(mu,ties.method="min")})))
wang_ranks_probs <- as.data.frame(apply(wang_ranks,2,function(ranks){unlist(lapply(1:11,function(j){mean(ranks==j)}))}))
wang_ranks_cumprobs <- as.data.frame(apply(wang_ranks_probs,2,cumsum))
names(wang_ranks) <- names(wang_ranks_probs) <- names(wang_ranks_cumprobs) <- treatments
# Figure 6
g9a <- ggplot(melt(cbind(rank=1:11,wang_ranks_probs),id.vars = 1),
aes(x=rank,y=factor(variable,levels=treatments[order(ybar)]),fill=value))+
geom_tile()+scale_x_continuous(breaks=1:11,limits=c(0.5,11.5))+
scale_y_discrete(limits=rev)+
scale_fill_gradient(low="white",high="black",limits=c(0,1))+
labs(x="Rank",y=element_blank(),fill="Probability ")+
theme_minimal()+theme(panel.grid = element_blank(),legend.position = "bottom")+
geom_text(data = melt(cbind(rank=1:11,wang_ranks_probs),id.vars = 1) %>% filter(rank==1),
aes(x=rank,y=variable,label=round(value,2)),
color=c(rep("black",10),"white"))
g9b <- create_clustermatrix(mcmc,treatments,1)+theme(legend.position="bottom")
plot_grid(plot_grid(g9a+theme(legend.position = "none"), g9b+theme(legend.position = "none"),
labels = c('A', 'B'), label_size = 12),
get_plot_component(g9a, 'guide-box-bottom', return_all = TRUE),nrow=2,rel_heights = c(.9,.1))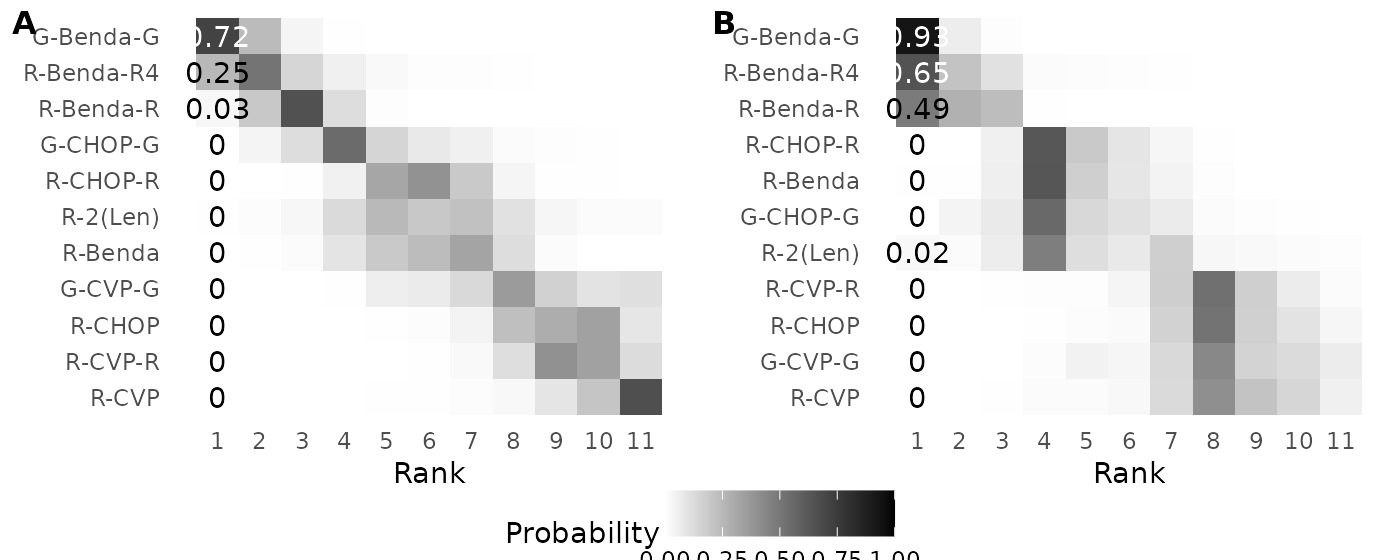
# Figure 7
g10a <- ggplot(melt(cbind(rank=1:11,wang_ranks_cumprobs),id.vars = 1),
aes(x=rank,y=value,color=factor(variable,levels=treatments[order(ybar)])))+
geom_line()+labs(x="Rank",y="Cumulative Probability",color=element_blank())+
theme_bw()+theme(panel.grid.minor = element_blank(),panel.grid.major.x = element_blank(),
legend.position = "bottom")+guides(color = guide_legend(nrow = 2))
g10b <- create_cumulativeranking(mcmc,treatments)
plot_grid(plot_grid(g10a+theme(legend.position = "none"), g10b+theme(legend.position = "none"),
labels = c('A', 'B'), label_size = 12),
get_plot_component(g10a, 'guide-box-bottom', return_all = TRUE),nrow=2,rel_heights = c(.85,.15))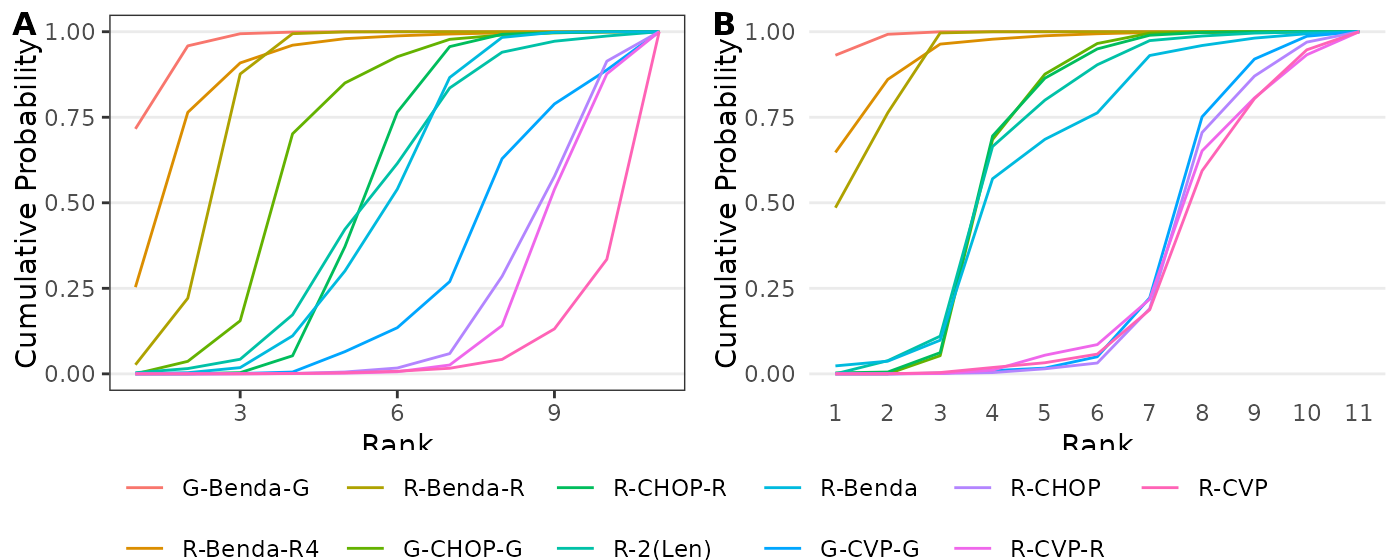
# Table 2
table2 <- data.frame(
SUCRA_Wang = apply(wang_ranks_cumprobs[1:10,],2,mean),
SUCRA_RaCE = apply(mcmc_ranks_cumprobs[1:10,],2,mean),
MNBT_Wang = apply(wang_ranks,2,function(ranks){
values <- quantile(ranks-1,c(0.5,0.25,0.75))
paste0(values[1]," (",values[2],", ",values[3],")")
}),
MNBT_RaCE = apply(mcmc_ranks,2,function(ranks){
values <- quantile(ranks-1,c(0.5,0.25,0.75))
paste0(values[1]," (",values[2],", ",values[3],")")
})
)
table2[order(ybar),]
## SUCRA_Wang SUCRA_RaCE MNBT_Wang MNBT_RaCE
## G-Benda-G 0.96674667 0.9923444 0 (0, 1) 0 (0, 0)
## R-Benda-R4 0.88424167 0.9427304 1 (0, 1) 0 (0, 1)
## R-Benda-R 0.81178500 0.9245186 2 (2, 2) 1 (0, 1)
## G-CHOP-G 0.66349833 0.6473594 3 (3, 4) 3 (3, 4)
## R-CHOP-R 0.51395000 0.6574624 5 (4, 5) 3 (3, 4)
## R-2(Len) 0.50069000 0.6042736 5 (4, 6) 3 (3, 5)
## R-Benda 0.48215000 0.6565974 5 (4, 6) 3 (3, 4)
## G-CVP-G 0.27813667 0.2760538 7 (6, 8) 7 (7, 8)
## R-CHOP 0.18591667 0.2787232 8 (7, 9) 7 (7, 8)
## R-CVP-R 0.15917167 0.2958426 8 (8, 9) 7 (7, 7)
## R-CVP 0.05371333 0.2644622 10 (9, 10) 7 (7, 8)The following code chunk reproduces the Figures 8–10 (Appendix B).
createtrace_K(mcmc)+
scale_x_continuous(breaks=seq(125000,250000,by=25000),
labels=paste0(c(125, 150, 175,200,225,250),"k"))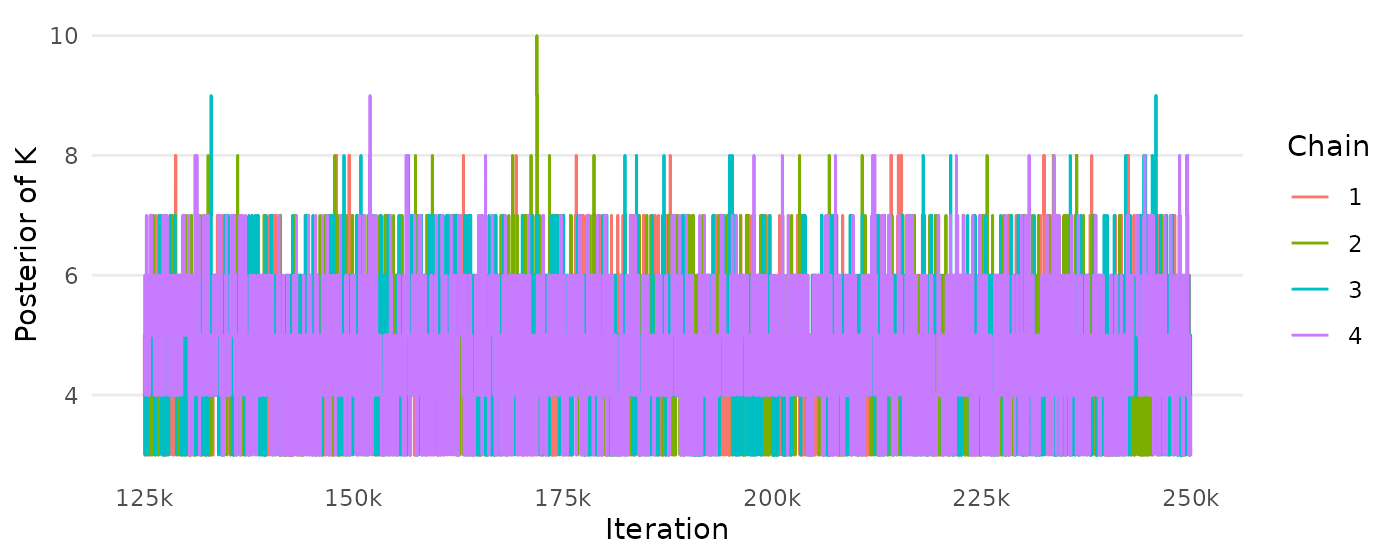
createtrace_mu(mcmc,names=treatments)+
scale_x_continuous(breaks=seq(125000,250000,by=25000),
labels=paste0(c(125, 150, 175,200,225,250),"k"))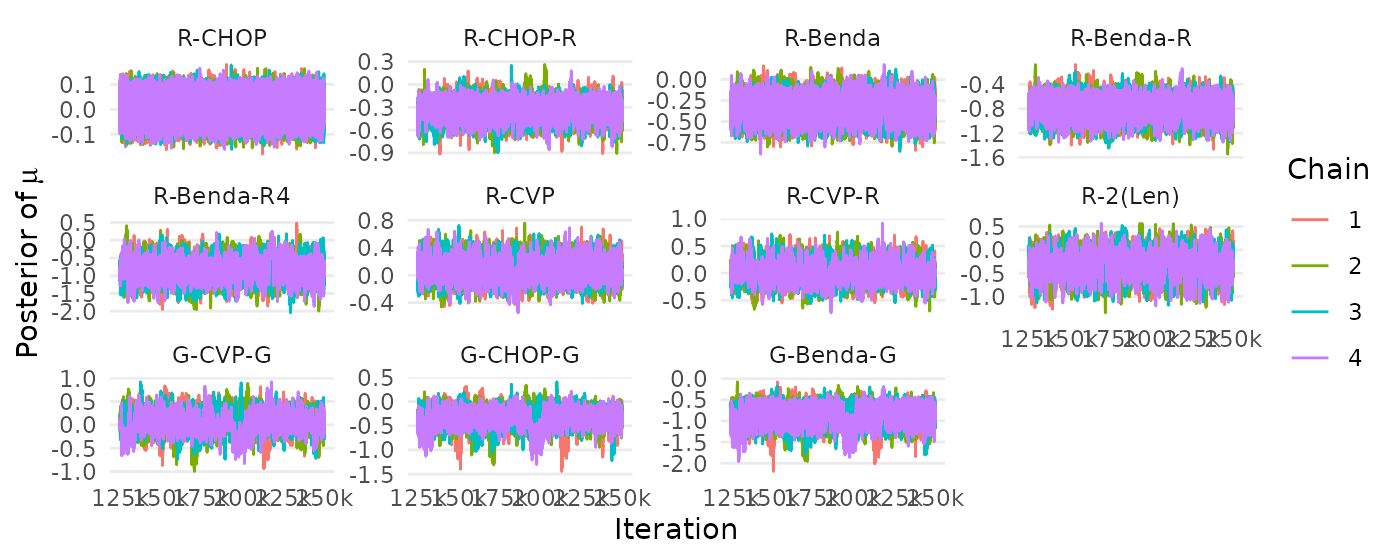
create_forestplot(mcmc,names=treatments)